The principle of operation and device RCD (residual current device)

For many, it is no longer news that a modern household electrical network must necessarily have RCD protection. For those who still do not know anything about such protective elements, let's say that this is the basis of human security. The device also helps prevent fires caused by electrical wiring. Therefore, acquaintance with this element of protection and automation will not be superfluous. Let's talk in detail about the device, what is it structurally made of and what is the principle of operation of the RCD?
Content
How does the leakage current occur?
Below we will consider what an RCD is needed for, but first, let's figure out what is a current leakage? The entire operation of the device is associated with this very concept.
In simple words, current leakage is called its flow from the phase conductor to the ground along a path that is undesirable and completely unauthorized for this. This can be the body of electrical equipment or household appliances, metal fittings or water pipes, damp plastered walls.
Leakage current occurs when insulation faults occur, which can occur for a number of reasons:
- aging as a result of long service life;
- mechanical damage;
- thermal effect in the case when electrical equipment operates in overload mode.
The danger of current leakage is that if the insulation of the electrical wiring is broken at the objects described above (the body of the device, the water pipe or the plastered damp wall), a potential will appear. If a person touches them, he will act as a conductor through which the current will go into the ground. The magnitude of this current can be such that it will cause the most sad consequences, up to and including death.
Video demonstration of RCD operation
How can you tell if your home has a leakage current? The first sign of this phenomenon will be the barely perceptible effect of electricity, that is, when you touch something, you seem to be slightly electrocuted. Most often, this dangerous phenomenon occurs in bathrooms. In order to guarantee yourself safety in your own apartment, it must be equipped with protective elements.
RCDs are used for this purpose (they are deciphered as residual current devices) or differential machines.
What is the basis of RCD tripping?
The principle of operation of the RCD is based on the measurement method. At the input and output, the readings of the currents flowing through the transformer are recorded.

If the input current reading is higher than the output, then there is a current leak somewhere in the circuit and the protective device is disabled. If these readings are the same, then the RCD will not trip.
Let us explain this principle in a little more detail for a two-wire and four-wire system. An RCD in a single-phase network does not work when currents of the same magnitude flow through the phase and neutral conductors. For a three-phase network, the same current readings in the neutral wire and the sum of the currents passing through the phase veins are required. In both versions of the network, when there is a difference in current values, this indicates an insulation breakdown. This means that a current leak will pass through this place, and the residual current device will work.
After this, the RCD cannot be turned on until the location of the damage is found.
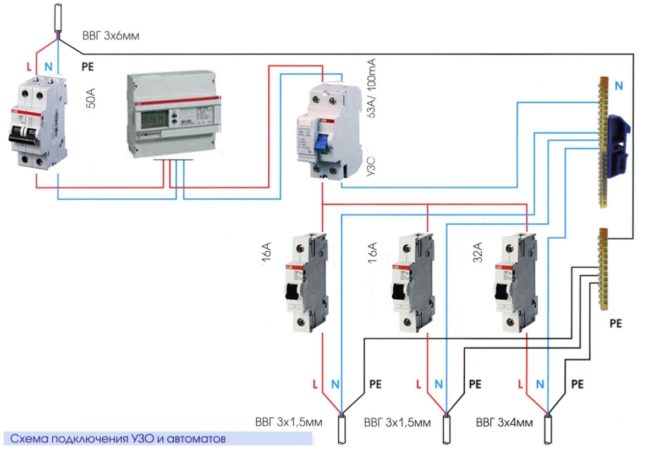
Let's translate all this theoretical principle of operation of an RCD into a practical example. A two-pole residual current device was installed in the home switchboard.An input two-core cable (phase and zero) is connected to its upper terminals. A zero with a phase is connected to the lower terminals, going to some kind of load, for example, to an outlet that feeds a water heating boiler.
Protective grounding of the boiler body is carried out with a wire bypassing the RCD.
If the power grid is in normal mode, then the movement of electrons is carried out along the phase wire from the input cable to the heating element of the boiler through the RCD. They move back to the ground again through the RCD, but already along the neutral wire.
The currents passing through the device have the same magnitude, but their direction is opposite (opposite).
Suppose a situation when insulation is damaged on the heating element. Now the current through the water will be partially on the boiler body, and then will go into the ground through the protective grounding wire. The rest of the current will return along the neutral wire through the RCD, only it will already be less than the incoming one exactly by the current leakage reading. This difference is determined by the RCD, and if the figure is higher than the trip setting, the device immediately reacts to an open circuit.
The same principle of operation and operation of an RCD, if a person touches a bare conductor or the body of a household appliance, on which a potential has appeared. A leakage current in such a situation occurs through the human body, the device instantly detects this and stops the supply of electricity by turning off.
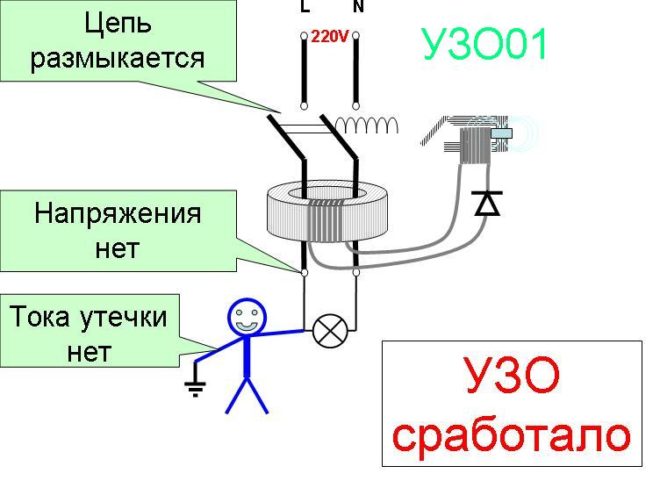
Serious injuries will not follow, because the RCD reacts almost instantly.
Structural performance
The design of the RCD will help us figure out how it reacts to current leakage. The main working units of the RCD are:
- Differential current transformer.
- The mechanism by which an electrical circuit breaks.
- Electromagnetic relay.
- Checking node.
The opposite windings are connected to the transformer - phase and zero. When the network is operating in normal mode, these conductors in the transformer core contribute to the induction of magnetic fluxes, which have opposite directions relative to each other. Due to the opposite direction, the total magnetic flux is zero.
The device and principle of operation of the RCD are clearly visible in the following video:
In the secondary transformer winding, an electromagnetic relay is connected; under normal operating conditions, it is at rest. A leakage current has occurred, and the picture changes immediately. Now, different current values begin to pass through the phase and neutral conductors. Accordingly, there will no longer be equal magnetic fluxes on the transformer core (they will be different both in magnitude and direction).
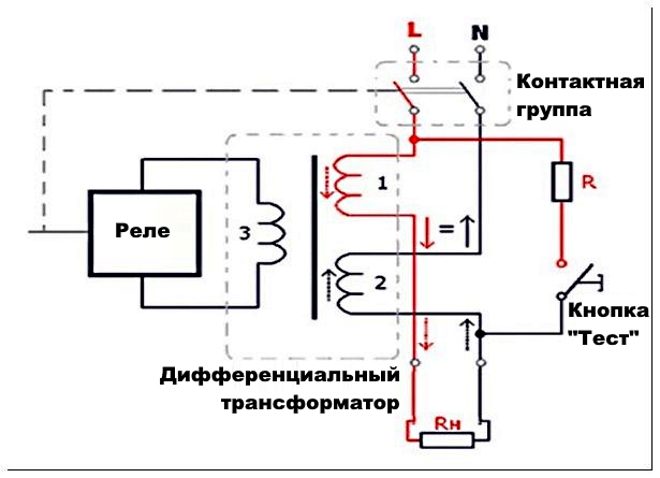
A current will appear in the secondary winding and, when its value reaches the set value, an electromagnetic relay will work. Its connection is made in conjunction with the release mechanism, it will instantly react and break the circuit.
The usual resistance serves as a test unit (some kind of load, the connection of which is made, bypassing the transformer). With this mechanism, a leakage current is simulated and the operable state of the device is checked. How does this check work?
There is a special button "TEST" on the RCD. Its main purpose is to supply current from the phase wire to the test resistance and then to the neutral conductor, bypassing the transformer. Due to the resistance, the current at the input and at the output will be different, and the created unbalance will trigger the shutdown mechanism. If the RCD did not turn off during the check, then you will have to abandon its installation.
The internal design of different RCD manufacturers may differ, but the general principle of operation remains unchanged.
All devices differ in the principle of operation. They are of electronic and electromechanical type.Electronic RCDs are distinguished by a complex circuit, they need additional power for operation. Electromechanical devices do not need external voltage.
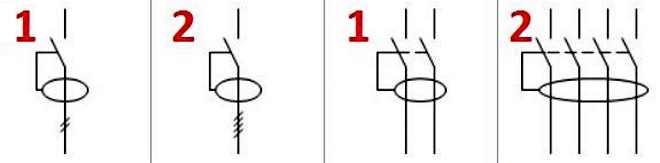
How is the RCD indicated on the diagram?
For connected RCDs, there are two generally accepted symbols in the diagrams.
Despite the structural complexity, we tried to make the designation of the device as simple as possible. There is nothing superfluous, only the following elements:
- A differential current transformer that is schematically depicted as a flattened ring.
- Poles (two for a single-phase network, four for a three-phase network).
- Switch acting on breaking contacts.
Moreover, it is the poles that have two types of designation:
- Sometimes they are drawn in straight vertical lines, depending on the number (two or four).
- In other cases, for reasons of compactness, one vertical straight line is drawn, and the number of poles is applied to it in the form of small oblique lines.
Basic performance characteristics of RCDs
In order for the device to work at the right time, it is necessary to select it correctly according to its performance characteristics and connect it.
- The main parameter is the value of the rated current. This is the maximum current that this device can withstand during a long operating period, while remaining in working condition and maintaining its protective characteristics. You will find this number on the front panel of the device, it must correspond to one of the readings in the standard row - 6, 10, 16, 25, 32, 40, 63, 80, 100 A. This RCD parameter depends on the load of the protected line and the cross-section of the conductors.
The RCD connection diagram provides for the joint installation of this device with circuit breakers.
It is important to remember this, because the RCD protects only against current leaks, and the machine will react to disconnection of the circuit in the mode of short circuit and overload.
The video shows whether it is possible to connect an RCD if there is no grounding in the apartment:
According to the rated current, the RCD must be selected an order of magnitude higher than the automatic device installed with it in a pair.
- Another important parameter is the rated residual current. This is the required value of the current leakage to disable the RCD. Differential currents also have a standard range, the values in it are normalized in milliamperes - 6, 10, 30, 100, 300, 500 mA. But on the RCD, this figure is indicated in amperes - respectively, 0.006, 0.01, 0.03, 0.1, 0.3, 0.5 A. You will also find this parameter on the device case.
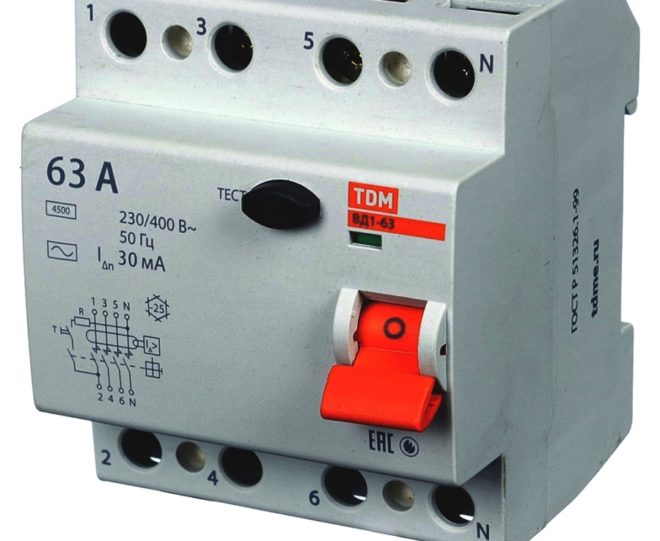

To protect people on the RCD, it is necessary to set the leakage current setting of 30 mA, because values that are higher will lead to injury, electrical injury and even death. Since the most dangerous environment is considered to be in humid rooms, then on the RCDs protecting them, a setting of 10 mA is selected.
We hope that by understanding the main purpose of the RCD and the principle of its operation, you will not neglect this important element of protection, and will make your life safe.