Overvoltage protection of 220 volts - how to protect electrical appliances in your home?

Although the supply of electricity to apartments and houses is regulated by law, residents should not fully rely on the appropriate services to provide the required quality of electricity. If, due to power surges, expensive electrical appliances fail, it will be almost impossible to get compensation. And since malfunctions on power lines are not uncommon, it is worthwhile to take measures on your own that will help protect household appliances from breakdown. To do this, overvoltage protection is needed, which can be provided by installing an appropriate device in the network - a protective relay, a sensor with an RCD or a voltage stabilizer.
Content
Acceptable electricity parameters
The voltage rating indicated on all household electrical appliances is 220V, but in real life this value is far from always stable. This is taken into account in the manufacture of modern devices, and they can operate stably with voltage fluctuations from 209 to 231V, and also tolerate a range from 198 to 242V. If small differences in potential were not provided for by the design of household appliances, it would break down constantly. Greater deviations lead to network congestion, and this reduces the operating life of the equipment.
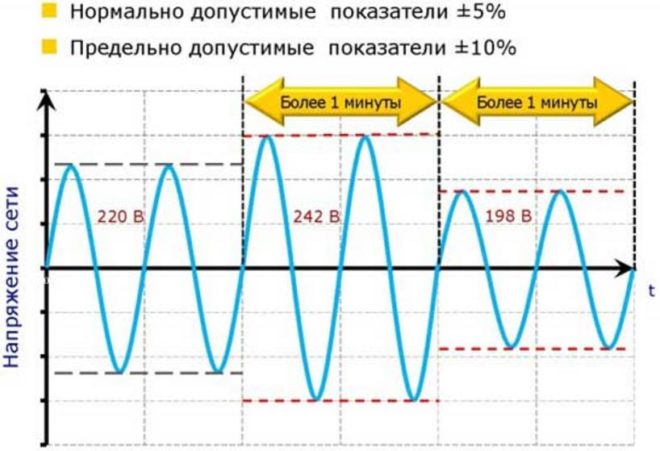
To smooth out voltage fluctuations and ensure the safety of devices, it is enough to install a stabilizer. Overvoltage is much more dangerous for electrical engineering (this is the name of a sharp jump in the potential difference).
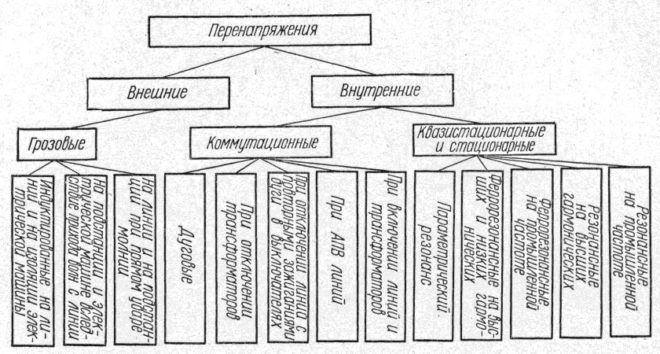
Varieties of overvoltage
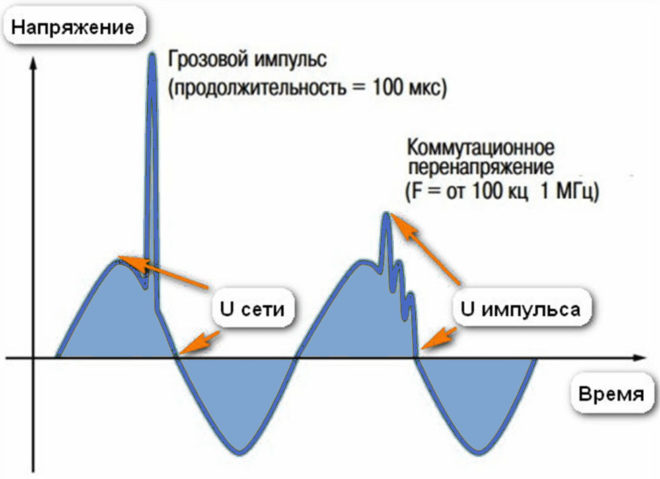
Overvoltage can last both short and long enough. It can be caused by a lightning strike during a thunderstorm or switching caused by a substation malfunction. To protect against them, an SPD (surge protection device) is connected to the 220 or 380 Volt network (domestic or industrial). Its automatic operation helps to secure the line when exposed to, for example, a powerful lightning discharge, from which the voltage stabilizer cannot save.
Visually about the SPD in the video:
A lightning strike leads to the appearance of a powerful electromagnetic pulse, under the influence of which electrical potentials arise in the conductors located near the discharge site, and a sharp voltage jump occurs. It lasts only about 0.1 s, but the potential difference is thousands of volts.
It is clear that when such a voltage enters the home and industrial networks, the consequences can be very serious.
Overvoltage due to switching
This phenomenon can occur when you turn on or turn off devices that give a high inductive load. These include power supplies, electric motors, and powerful mains-powered tools.
This effect is due to the laws of commutation. An instantaneous change in the magnitude of the current in the solenoid, as well as the potential difference across the capacitor, cannot occur. When a circuit with such a load is connected or opened, the appearance of an electric potential caused by self-induction and switching processes is noted at the point of contact.
The transient process is always accompanied by a voltage surge that has the opposite polarity to the input voltage.The small capacitance of the conductors in the network causes a resonance that lasts a short time and causes high frequency oscillations. At the end of the transient, they decay.
How long the overvoltage will last and what its magnitude will be depends on the following indicators:
- Load inductance.
- The instantaneous value of the potential difference during switching.
- The capacity of the connecting electrical cables.
- Reactive power.
Danger of overvoltage
Since the insulation of the wires is designed for a voltage value that is significantly higher than the nominal, breakdown usually does not occur. If the electrical impulse acts for a short time, then the voltage at the output of the power supplies with a stabilizer does not have time to increase to a critical indicator. The same applies to ordinary bulbs - if the sharply increased voltage quickly normalizes, then the spiral does not have time not only to burn out, but even to overheat.
If the insulating layer cannot withstand the increased voltage and its breakdown occurs, then an electric arc appears. In this case, the flow of electrons penetrates through the microcracks that have arisen in the insulation, and goes through the gases that fill the formed smallest voids. And a large amount of heat generated by the arc promotes the expansion of the conductive channel. As a result, the current builds up gradually, and the circuit breaker trips with some delay. And although it only takes a few moments, they are quite enough for the wiring to fail.

What devices provide network overvoltage protection?
An electrical line surge protection circuit may include:
- Lightning protection system.
- Voltage regulator.
- Overvoltage sensor (installed together with RCD).
- Overvoltage relay.
Separately, it must be said about uninterruptible power supplies, through which computers are most often connected in home networks. This appliance is not designed to provide overvoltage protection in the network. Its function is different: when the light is suddenly turned off, it works like a battery, allowing the user to save information and quietly turn off the PC. Therefore, it should not be confused with a voltage regulator.
The principle of operation of protective devices
To protect against electrical impulses generated by lightning, a lightning arrester is installed together with an SPD. And to protect the line from the flow of electrons, the parameters of which do not correspond to the operating characteristics of the network, you can use special sensors, as well as an overvoltage relay.
It should be said that both the DPN and the relay differ from the stabilizer in principle of operation and purpose.
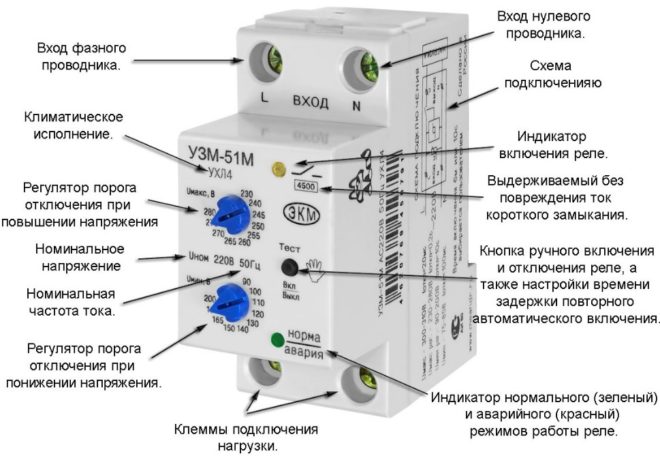
The task of these elements is to stop the supply of electricity in case the value of the difference exceeds the maximum threshold specified in the technical passport of the protective equipment or set by the regulator.
After the parameters of the electric line are normalized, the relay is switched on independently. DPN for line protection should be installed only in tandem with a residual current device. Its task is to cause a leakage current when a malfunction is detected, under the influence of which the RCD will trip.
Visually about the voltage relay in the video:
The disadvantage of such a circuit is the need to manually turn it on after the voltage returns to normal. In this regard, the voltage regulator compares favorably. This device provides an adjustable time delay for the current flow if it is triggered by excessive voltage. The stabilizer is often used to connect air conditioners and refrigerators.
Long-term overvoltage
Long-term overvoltages very often occur due to a break in the neutral conductor.The uneven load on the phase conductors becomes the cause of phase imbalance - the displacement of the potential difference to the conductor with the largest load.
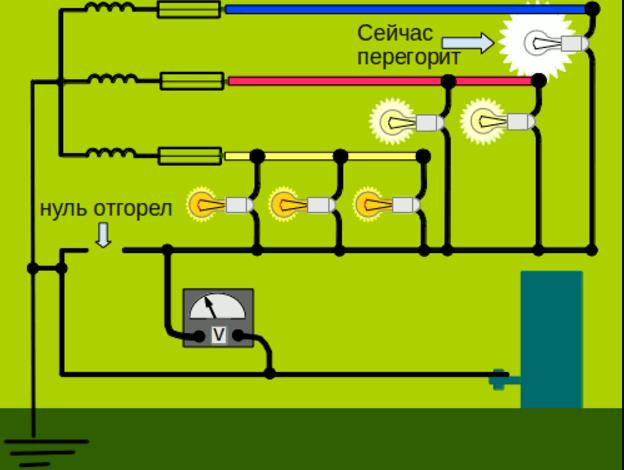
In other words, under the influence of an uneven three-phase electric current, voltage begins to accumulate on a zero cable that does not have grounding. The situation does not return to normal until a repeated accident finally destroys the line or a specialist eliminates the malfunction.
If the neutral wire in the electrical outlet is broken, the voltage will change in accordance with the load, which users who do not know about the problems will connect to different phases. It is almost impossible to use a faulty circuit, even if a good stabilizer is included in the power line. The fact is that network parameters that regularly go beyond the stabilization limits will lead to the device being constantly turned off.
Clearly about the zero break and what needs to be done at the same time - in the video:
Lack of voltage (dip)
This phenomenon is especially familiar to people living in villages and villages. A dip (subsidence) is a voltage drop below the allowable limit.
The danger of subsidence lies in the fact that the design of many household appliances includes several power supplies, and a lack of voltage will lead to the fact that one of them will turn off for a short time. The device will react to this by issuing an error on the display and stopping work.

If we are talking about a heating boiler, and the malfunction occurred in the winter, then the house will remain without heating. Connecting a stabilizer will help to avoid this situation. This device, having fixed the subsidence, will increase the voltage value to the nominal value. The stabilizer can save the situation, even if the voltage in the network has dropped due to the fault of the transformer substation.
Conclusion
In this article, we told you why you need overvoltage protection in the network, what devices it is provided and how to use them correctly. The recommendations given will help readers understand the causes of a mains voltage failure, as well as select and install a device for protecting the mains.