Technical characteristics and application of wire PUGNP
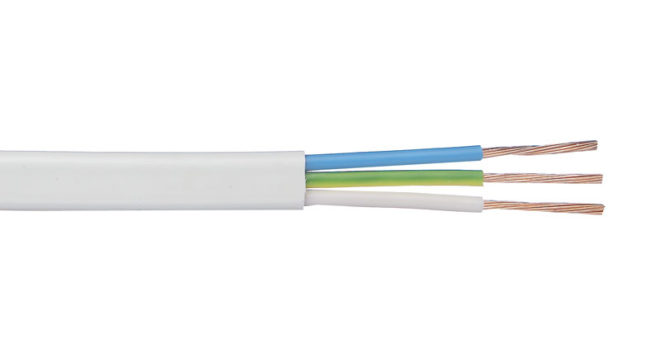
The PUGNP electrical wire is a type of the common PUNP electrical wire, with the difference that it uses flexible rather than solid conductors. Both of these cables are widely used due to their relative cheapness, compared to the recommended VVG or NYM. But when purchasing it, it must be borne in mind that the cable ПУГНП and ПУНП is prohibited for use by the provisions of the PUE, as fire hazardous.
Content
What is PUGNP

Two or three-core copper cable, the cores of which are recruited from at least seven conductive threads, twisted together. The insulation of each core is made with a thickness of at least 0.3 mm and is made in a separate color. If it is a two-core cable, then one of the cores will have a blue color for zero, and in a three-core cable there will be a yellow ground wire with a green stripe. However, you can find other colors, but the insulation of the cores in any case will differ from each other. The thickness of the outer, general insulation is 0.5 mm - it is made of white or unpainted PVC plastic.
The technical characteristics define the conductors of wires as conductors of electric current with a voltage not exceeding 250 Volts and a frequency of 50 Hertz. Their cross-section ranges from 0.75 to 4 mm², which allows you to choose a cable for most household needs.
Explanation of the abbreviation
A distinctive feature of PUNP and PUGNP is their flat shape, which is directly reflected in the abbreviation. For a wire of the PUNP brand, the decoding of the name looks like "P" - a wire (although in fact it is a cable), "UN" - universal (without special restrictions in the fields of application), "P" - flat (the cores are located not in a circle, but next to each other with a friend). If the abbreviation looks like "APUNP", then the conductors are made of aluminum.

Accordingly, the decoding of the PUGNP wire reads as "P" - wire, "UN" - universal, "G" - flexible, "P" - flat. Due to the fact that this cable is flexible, aluminum is not used in its manufacture, therefore there is no prefix "A" in front of the name, but it still has additional varieties. This is PUNGPng, with an insulating coating of low flammability and PUGNPngd-LS, which, besides not burning, also does not smolder.
Why in the name of the wire the letter "G" is not in its place, one can only guess - perhaps this is a trivial mistake when registering the name, or maybe someone thought it was more consonant.
There will definitely not be official comments on this topic, since the PUGNP is prohibited for use, due to its inconsistency with modern fire safety requirements. True, "cannot be used" does not mean prohibiting production, which is still being done due to its high popularity due to its low cost.
With production, everything is also interesting - the PUGNP does not have to be marked by the manufacturer (it is affixed only on labels that are attached to a solid coil of wire). Accordingly, even if all the technical characteristics, GOSTs and TUs are known, their implementation is difficult to control and no one guarantees it.
Specifications and operating conditions

Manufacturing takes place according to TU 16K13-020-93 state standard. The purpose of the PUGNP was defined as laying lighting and supplying low-power electrical devices operating in electrical networks with voltages up to 250 Volts. The laying method is fixed. The main technical characteristics are as follows:
- The conductor material is copper.
- Insulation material - PVC compound.
- The operating temperature at which the insulation properties are preserved is from -50 to +50 C °.Safety factor up to +70 C ° - the cable must withstand prolonged heating to this temperature and short-term up to +80.
- The temperature at which it is allowed to perform installation is from -15. Lower values increase the likelihood of insulation breakage when the wire is bent.
- Medium elasticity - when laying, bends with a radius less than 10 outer diameters of the cable are prohibited.
- Permissible ambient humidity - 100%, at temperatures up to +35 C °.
- Resistance of a core with a cross-section of 1 mm² - up to 27.1 Ohm, cores 1.5 mm² - up to 12.1 Ohm, cores 2.5 mm² - up to 7.41 Ohm and cores 4 mm² - 4.61 Ohm. In test measurements, this parameter is calculated at a temperature of 20 ° C, on a control cable section 1 km long.
- Estimated service life - 15 years.
- Marking - ПУГНП X * Y, where X is the number of cores, and Y is their cross-section.
- The PUNGPng marking indicates increased resistance to fire, PUGNPngd-LS - a reduced smoke emission during smoldering.
- The warranty period is 2 years from the date of the start of operation.
For using the wire, see this video:
Reasons for the ban on use
First of all, the PUGNP wire does not meet the requirements for conductor insulation thickness. If the PUE requirements unambiguously indicate the need to use a sheath with a minimum thickness of 0.4-0.5 mm, the factory TU permits the use of a 0.3 mm plastic compound layer.
In addition, TU 16.K13-020-93 refers rather freely to the tolerances in the cross-section of the conductors - the allowed error is 30%. As a result, if a 2.5 mm² cable is purchased, then in fact inside it there may be wires with conductors 2.5 - 30% = 1.75 mm². It is clear that when even the rated load is connected to it, the cable may not withstand and melt. According to statistics, more than 50% of all wire fires occurred precisely when using the PUNP and PUGNP brands.
Briefly about the main
The PUGNP cable is manufactured according to outdated specifications that do not meet modern safety standards and its use is prohibited by the requirements of the PUE. Accordingly, the decision to purchase it or not is taken entirely at your own peril and risk, because in the event of an unforeseen situation, the examination will show that the wrong wire was used.
If, for some reason, it has to be used, then one must remember about the tolerances that exist in the specifications for which the cable is manufactured, and all calculations should be made as if the cross-section of the conductors is less than the specified nominal by 30%. When the cable is laid externally, it must be placed in a corrugation, the ends of which are wrapped with electrical tape to prevent air from entering. In this case, even with significant overheating, the wire will not light up, since there will be no oxygen access.
Particularly meticulous buyers come for a cable with a micrometer and check the cross-section of the conductors on the spot. This is a good, but rather relative method, because the test is performed on a local section of the wire, and no one can guarantee that the results obtained will be the same throughout its length.




